Monday, August 28, 2006
Ear model pics
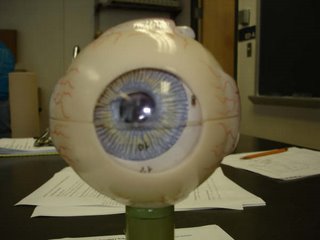
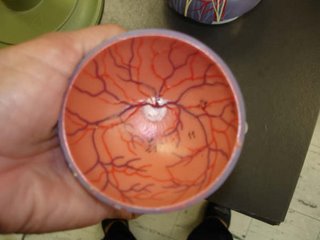
Eye model pics
Sunday, August 06, 2006
Syllabus for Biol 318 in Fall 2006
Biology 318: Advances Human Anatomy and Physiology
Instructor: Dr. Pegge Alciatore
Office: 108 Billeaud Hall Phone: 482-5234 E-Mail: pla7994@louisiana.edu
318. Advanced Human Anatomy and Physiology (3,2,4). Cat anatomy and advanced
principles of human physiology as they pertain to all body systems. Prereq:
Biology 220 and 221 or equivalent introductory course with a grade of C or better.
Text: K. Saladin, Anatomy and Physiology, 4th Edition. McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., Inc.
POLICIES FOR BIOLOGY 318 LECTURE:
1. Daily attendance is expected. If you miss more than five classes in the semester you may be asked to withdraw from the course. You are required to sign the attendance role every class period.
2. Absence from a scheduled exam will require an excuse acceptable to the instructor. Make-up exams will be given at the end of the semester. It is the responsibility of the student to make arrangements for make-up tests. If student fails to do so, a zero will be average into the grade. The makeup exam is subjective.
Grading Scale: A = 90-100
B = 80-89
C = 70-79
D = 60-69
F = below 60
3. Lecture is worth two-thirds of the total grade.
4. Examinations in lecture (date TBA):
Test 1: Nervous System
Endocrine System 100 points
Test 2: Respiratory System
Cardiovascular System 100 points
Test 3: Digestive System
Urinary System 100 points
Test 4: Reproductive System
Lymphatic System 100 points
The first three tests will consist of a combination of multiple-choice items, and short answer essay questions. The final and fourth test will be given during finals time and will be 50 multiple-choice questions. The final is not comprehensive and 60 minutes will be allowed to take the exam. If cheating is observed, the student will receive a zero and his/her name will be reported to the Dean of Students Services. Cheating can be cited on the students’ academic record.
5. EMERGENCY EVACUATION PROCEDURES. A map of the floor is posted near the elevator marking the designated rescue area. This is an area where emergency service personnel will go first to look for individuals who need assistance in exiting the building. The Coordinator of Services to Students with Disabilities, University Police, Lafayette City Police and Fire Departments will be provided with maps of Designated Rescue Areas for all University buildings. Students who need assistance should identify themselves to the teaching faculty.
LECTURE TOPICS:
It is assumed that the principles and concepts learned in Biology 220/221 were and continue to be understood. This information will provide a sound, solid basis upon which to grown in an understanding of anatomy and physiology.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST I:
Nervous System
1. Energy transformation in receptors.
2. Transmission of impulses along neurons.
3. Interpretation of action potentials at neuronal junctions.
4. Spinal cord control over survival reflexes.
5. Chemistry and actions of neurotransmitters.
6. Types of synapsis.
7. Cellular membrane receptors and how they differ from energy transforming receptors.
8. Role of gray matter as in spinal cord, medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, diencephalons, cerebrum, and cerebellum.
9. Ascending sensory tracts and descending motor tracts.
10. Meninges and their jobs.
11. CSF formation in ventricles and its circulation into the dural sinuses.
12. Special functions of: cerebral cortex, basal nuclei, limbic system, reticular formation, RAS, etc.
13. Autonomic nervous system structure and function.
Endocrine System
1. cAMP versus gene activating methods of hormone action.
2. Neuronal, hormonal, and hypothalamic-anterior pituitary methods of hormonal control.
3. Anatomy of hypothalamus as it relates to the anterior and posterior pituitary.
4. Supraoptic and Paraventricular nuclei: their structure, function, action, and control.
5. Role of Growth Hormone and Prolactin.
6. Hypothalamic factors: chemistry and release.
7. Factor influences on anterior pituitary.
8. Influence of anterior pituitary hormones on: thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pineal, adrenal cortex, thymus etc. General anatomy of these glands.
9. Role of positive and negative feedback mechanisms in normal endocrine action.
10. Products of thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pineal, adrenal cortex, thymus, etc. and their influences on physiology and homeostasis.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST II:
Respiratory System
1. Review of organs of respiratory system and unique histology.
2. Mechanics of inspiration and expiration.
3. Control of respiration by the medullary rhythmicity center and the pons.
4. The effects of other factors, such as blood gas composition, pH, temperature, etc.
5. Respiratory membrane histology.
6. Gas exchange through the respiratory membrane (partial pressure of gases, laws of physics as they apply).
7. Pulmonary circulation and its uniqueness.
8. Transportation of gases in the blood.
9. Utilization of oxygen (cellular respiration review).
10. Hormonal and nervous system influences on respiration.
Blood and Cardiovascular System
1. Review of blood cells and plasma composition (what does blood do for you?).
2. Review of heart anatomy and unique histology of cardiac muscle tissue.
3. Discussion of conduction pathway parts as they regulate heart beat and rate.
4. Relation of conduction pathway to an ECG reading.
5. Heart action and blood flow (hemodynamics)
6. Blood pressure (normal and abnormal—high BP the silent killer).
7. Review stroke volume, pulse pressure, cardiac output, mean arterial BP etc.
8. Pathways of circulation (systemic, pulmonary, hepatic portal and microcirculation).
9. Distinguish between arteries, veins, and capillaries in function and structure.
10. Capillaries: meals on wheels and Dempster dumsters.
11. Nervous and hormonal influences on the CV system.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST III:
Digestive System
1. Review organs and accessory organs of the digestive system. Be able to trace
a morsel of food from mouth to anus describing what each part does specifically.
2. Describe histology of the alimentary canal, in general, and as it differs from
one subpart to another (how does histology dictate function?).
3. Understand basic chemistry and physiology of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, minerals and vitamins found in a balanced diet.
4. Answer the question “Why do we eat?”
5. Salivary glands and their contribution to digestion.
6. Thoroughly understand the role, nature, and composition of enzymes used in the process of chemical digestion. Enzyme-Substrate Complex—What’s really happening?
7. How does chemical digestion differ from physical?
8. How does food move through the system (myenteric plexus)? Types of movement (peristalsis, segmentation, swallowing, mass movement, defecation).
9. Role of the liver in digestion and bile formation.
10. Pancreatic juices (where are they made, how are they transported and what do they do?)
11. Hormonal control in digestion (gastrins, CCK, secretin, histamines, GIP etc.).
12. Nervous system control over digestion.
13. Large intestine: structure and function.
Urinary System
1. Review organs of the urinary system: kidneys (retroperitoneal), ureters,
urinary bladder, urethra).
2. Study unique histology of the various parts of the urinary systems (e.g.
transitional epithelium, detrusor muscle, rugae of the urinary bladder and
unique histology of dct, pct, loop of Henle and collecting ducts).
3. Relate kidneys to the blood (composition, volume, and pH of blood).
4. Describe the anatomy of the kidney as it relates to the blood vessels entering and leaving the kidney.
5. Draw, describe and explain cortical and juxtamedullary nephron units.
6. How do we make urine: filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion.
7. What is in urine? What shouldn’t be in urine?
8. How do we physically void?
9. Describe role of kidney in acid/base balance and electrolyte balance.
10. How do we regulate water loss on a hot day?
11. How does the nervous and endocrine systems regulate the activities of the kidneys (hypothalamus and ADH/Aldosterone/Angiotensin II/countercurrent multiplier effect etc.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST IV:
Reproductive System
1. General review of organs of male reproductive systems (testicle, seminiferous
tubules, rete testis, epididymus, spermatic cord, vas deferens, accessory glands, urethra.
2. General review of organs of female reproductive system (ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina).
3. Extensive histology of ovary and testis (emphasis on ovarian cortex and the seminiferous tubule).
4. Description of male reproductive physiology (spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis, motility, and capacitation.
5. Discussion of female reproductive physiology (ovarian—follicle development and menstrual cycles—endometrial changes).
6. Understand the role of hypothalamus and anterior pituitary in the regulation of male and female reproductive physiology.
7. Explanation of fertilization, cleavage, implantation, embryo and fetal stages of reproduction.
Lymphatic System
1. Discussion of the five general functions of the lymphatic system.
a. Dry cell.
b. Fat transport and lacteals
c. Lymphocytes for defense
d. Development of immunity
e. Phagocytosis
2. Review of the organs of the lymphatic system and their functions: lymph nodes, vessels, tonsils, thymus, spleen, and lymph fluid.
3. Emphasis on tissue fluid regulation—edema.
4. Immunity—specific and nonspecific defense against pathogens.
5. Nonspecific defense: mechanical factors, chemical factors, antimicrobial factors (interferon, and complement) and phagocytosis.
6. Specific immunity: Cellular immunity (T-cell---Cytotoxic killer T-cells, Helper T-cells, Hypersensitive T-cells, and Suppressor T-cells).
7. Specific immunity: Humoral immunity (B-cell—plasma cells and memory cells.
Instructor: Dr. Pegge Alciatore
Office: 108 Billeaud Hall Phone: 482-5234 E-Mail: pla7994@louisiana.edu
318. Advanced Human Anatomy and Physiology (3,2,4). Cat anatomy and advanced
principles of human physiology as they pertain to all body systems. Prereq:
Biology 220 and 221 or equivalent introductory course with a grade of C or better.
Text: K. Saladin, Anatomy and Physiology, 4th Edition. McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., Inc.
POLICIES FOR BIOLOGY 318 LECTURE:
1. Daily attendance is expected. If you miss more than five classes in the semester you may be asked to withdraw from the course. You are required to sign the attendance role every class period.
2. Absence from a scheduled exam will require an excuse acceptable to the instructor. Make-up exams will be given at the end of the semester. It is the responsibility of the student to make arrangements for make-up tests. If student fails to do so, a zero will be average into the grade. The makeup exam is subjective.
Grading Scale: A = 90-100
B = 80-89
C = 70-79
D = 60-69
F = below 60
3. Lecture is worth two-thirds of the total grade.
4. Examinations in lecture (date TBA):
Test 1: Nervous System
Endocrine System 100 points
Test 2: Respiratory System
Cardiovascular System 100 points
Test 3: Digestive System
Urinary System 100 points
Test 4: Reproductive System
Lymphatic System 100 points
The first three tests will consist of a combination of multiple-choice items, and short answer essay questions. The final and fourth test will be given during finals time and will be 50 multiple-choice questions. The final is not comprehensive and 60 minutes will be allowed to take the exam. If cheating is observed, the student will receive a zero and his/her name will be reported to the Dean of Students Services. Cheating can be cited on the students’ academic record.
5. EMERGENCY EVACUATION PROCEDURES. A map of the floor is posted near the elevator marking the designated rescue area. This is an area where emergency service personnel will go first to look for individuals who need assistance in exiting the building. The Coordinator of Services to Students with Disabilities, University Police, Lafayette City Police and Fire Departments will be provided with maps of Designated Rescue Areas for all University buildings. Students who need assistance should identify themselves to the teaching faculty.
LECTURE TOPICS:
It is assumed that the principles and concepts learned in Biology 220/221 were and continue to be understood. This information will provide a sound, solid basis upon which to grown in an understanding of anatomy and physiology.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST I:
Nervous System
1. Energy transformation in receptors.
2. Transmission of impulses along neurons.
3. Interpretation of action potentials at neuronal junctions.
4. Spinal cord control over survival reflexes.
5. Chemistry and actions of neurotransmitters.
6. Types of synapsis.
7. Cellular membrane receptors and how they differ from energy transforming receptors.
8. Role of gray matter as in spinal cord, medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, diencephalons, cerebrum, and cerebellum.
9. Ascending sensory tracts and descending motor tracts.
10. Meninges and their jobs.
11. CSF formation in ventricles and its circulation into the dural sinuses.
12. Special functions of: cerebral cortex, basal nuclei, limbic system, reticular formation, RAS, etc.
13. Autonomic nervous system structure and function.
Endocrine System
1. cAMP versus gene activating methods of hormone action.
2. Neuronal, hormonal, and hypothalamic-anterior pituitary methods of hormonal control.
3. Anatomy of hypothalamus as it relates to the anterior and posterior pituitary.
4. Supraoptic and Paraventricular nuclei: their structure, function, action, and control.
5. Role of Growth Hormone and Prolactin.
6. Hypothalamic factors: chemistry and release.
7. Factor influences on anterior pituitary.
8. Influence of anterior pituitary hormones on: thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pineal, adrenal cortex, thymus etc. General anatomy of these glands.
9. Role of positive and negative feedback mechanisms in normal endocrine action.
10. Products of thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pineal, adrenal cortex, thymus, etc. and their influences on physiology and homeostasis.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST II:
Respiratory System
1. Review of organs of respiratory system and unique histology.
2. Mechanics of inspiration and expiration.
3. Control of respiration by the medullary rhythmicity center and the pons.
4. The effects of other factors, such as blood gas composition, pH, temperature, etc.
5. Respiratory membrane histology.
6. Gas exchange through the respiratory membrane (partial pressure of gases, laws of physics as they apply).
7. Pulmonary circulation and its uniqueness.
8. Transportation of gases in the blood.
9. Utilization of oxygen (cellular respiration review).
10. Hormonal and nervous system influences on respiration.
Blood and Cardiovascular System
1. Review of blood cells and plasma composition (what does blood do for you?).
2. Review of heart anatomy and unique histology of cardiac muscle tissue.
3. Discussion of conduction pathway parts as they regulate heart beat and rate.
4. Relation of conduction pathway to an ECG reading.
5. Heart action and blood flow (hemodynamics)
6. Blood pressure (normal and abnormal—high BP the silent killer).
7. Review stroke volume, pulse pressure, cardiac output, mean arterial BP etc.
8. Pathways of circulation (systemic, pulmonary, hepatic portal and microcirculation).
9. Distinguish between arteries, veins, and capillaries in function and structure.
10. Capillaries: meals on wheels and Dempster dumsters.
11. Nervous and hormonal influences on the CV system.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST III:
Digestive System
1. Review organs and accessory organs of the digestive system. Be able to trace
a morsel of food from mouth to anus describing what each part does specifically.
2. Describe histology of the alimentary canal, in general, and as it differs from
one subpart to another (how does histology dictate function?).
3. Understand basic chemistry and physiology of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, minerals and vitamins found in a balanced diet.
4. Answer the question “Why do we eat?”
5. Salivary glands and their contribution to digestion.
6. Thoroughly understand the role, nature, and composition of enzymes used in the process of chemical digestion. Enzyme-Substrate Complex—What’s really happening?
7. How does chemical digestion differ from physical?
8. How does food move through the system (myenteric plexus)? Types of movement (peristalsis, segmentation, swallowing, mass movement, defecation).
9. Role of the liver in digestion and bile formation.
10. Pancreatic juices (where are they made, how are they transported and what do they do?)
11. Hormonal control in digestion (gastrins, CCK, secretin, histamines, GIP etc.).
12. Nervous system control over digestion.
13. Large intestine: structure and function.
Urinary System
1. Review organs of the urinary system: kidneys (retroperitoneal), ureters,
urinary bladder, urethra).
2. Study unique histology of the various parts of the urinary systems (e.g.
transitional epithelium, detrusor muscle, rugae of the urinary bladder and
unique histology of dct, pct, loop of Henle and collecting ducts).
3. Relate kidneys to the blood (composition, volume, and pH of blood).
4. Describe the anatomy of the kidney as it relates to the blood vessels entering and leaving the kidney.
5. Draw, describe and explain cortical and juxtamedullary nephron units.
6. How do we make urine: filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion.
7. What is in urine? What shouldn’t be in urine?
8. How do we physically void?
9. Describe role of kidney in acid/base balance and electrolyte balance.
10. How do we regulate water loss on a hot day?
11. How does the nervous and endocrine systems regulate the activities of the kidneys (hypothalamus and ADH/Aldosterone/Angiotensin II/countercurrent multiplier effect etc.
GENERAL TOPICS FOR TEST IV:
Reproductive System
1. General review of organs of male reproductive systems (testicle, seminiferous
tubules, rete testis, epididymus, spermatic cord, vas deferens, accessory glands, urethra.
2. General review of organs of female reproductive system (ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina).
3. Extensive histology of ovary and testis (emphasis on ovarian cortex and the seminiferous tubule).
4. Description of male reproductive physiology (spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis, motility, and capacitation.
5. Discussion of female reproductive physiology (ovarian—follicle development and menstrual cycles—endometrial changes).
6. Understand the role of hypothalamus and anterior pituitary in the regulation of male and female reproductive physiology.
7. Explanation of fertilization, cleavage, implantation, embryo and fetal stages of reproduction.
Lymphatic System
1. Discussion of the five general functions of the lymphatic system.
a. Dry cell.
b. Fat transport and lacteals
c. Lymphocytes for defense
d. Development of immunity
e. Phagocytosis
2. Review of the organs of the lymphatic system and their functions: lymph nodes, vessels, tonsils, thymus, spleen, and lymph fluid.
3. Emphasis on tissue fluid regulation—edema.
4. Immunity—specific and nonspecific defense against pathogens.
5. Nonspecific defense: mechanical factors, chemical factors, antimicrobial factors (interferon, and complement) and phagocytosis.
6. Specific immunity: Cellular immunity (T-cell---Cytotoxic killer T-cells, Helper T-cells, Hypersensitive T-cells, and Suppressor T-cells).
7. Specific immunity: Humoral immunity (B-cell—plasma cells and memory cells.